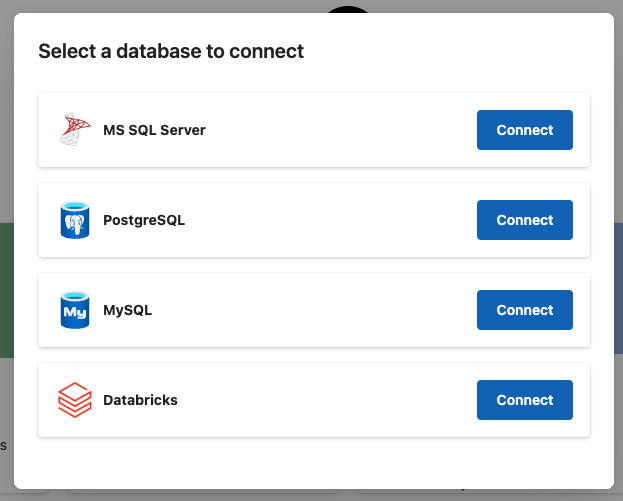
Zebra AI offers several direct SQL connectors so you can work with data where it lives in the cloud—no file exports needed. You can connect, browse schemas, run safe SELECT queries, preview results, and use them in stories.
Supported connectors (excluding Power BI)
- MSSQL (SQL Server)
- PostgreSQL
- MySQL
- Databricks SQL
- OneLake Warehouse (Zebra AI Workload for Fabric only)
Authentication at a glance
- MSSQL: Microsoft Entra ID (Azure AD) token (consent window), Username/Password
- OneLake Warehouse: Microsoft Entra ID (Azure AD) token (automatically retrieved after consent is granted)
- PostgreSQL, MySQL: Username/Password
- Databricks: Personal Access Token + HTTP Path (+ Catalog/Schema)
What the experience looks like
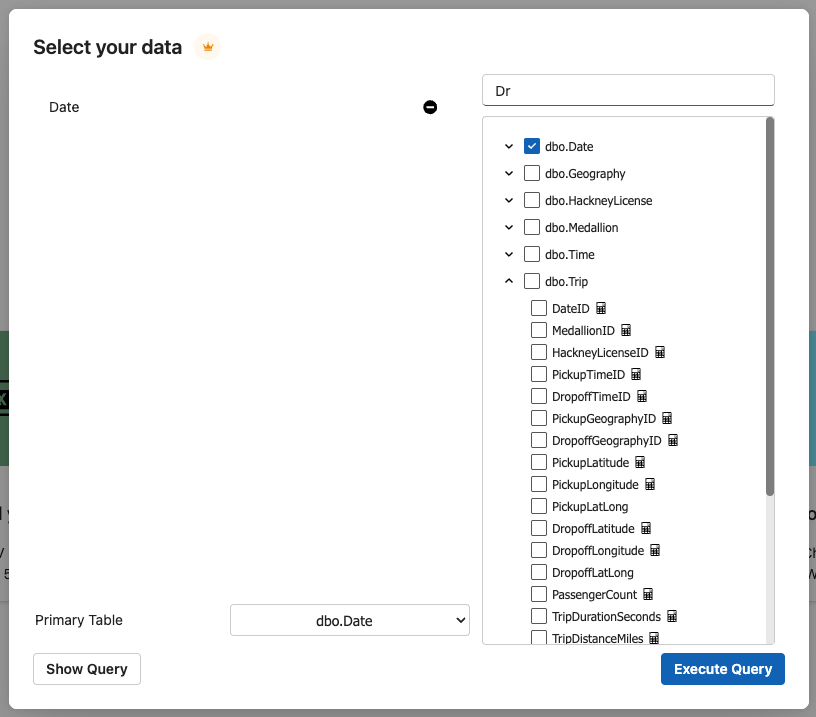
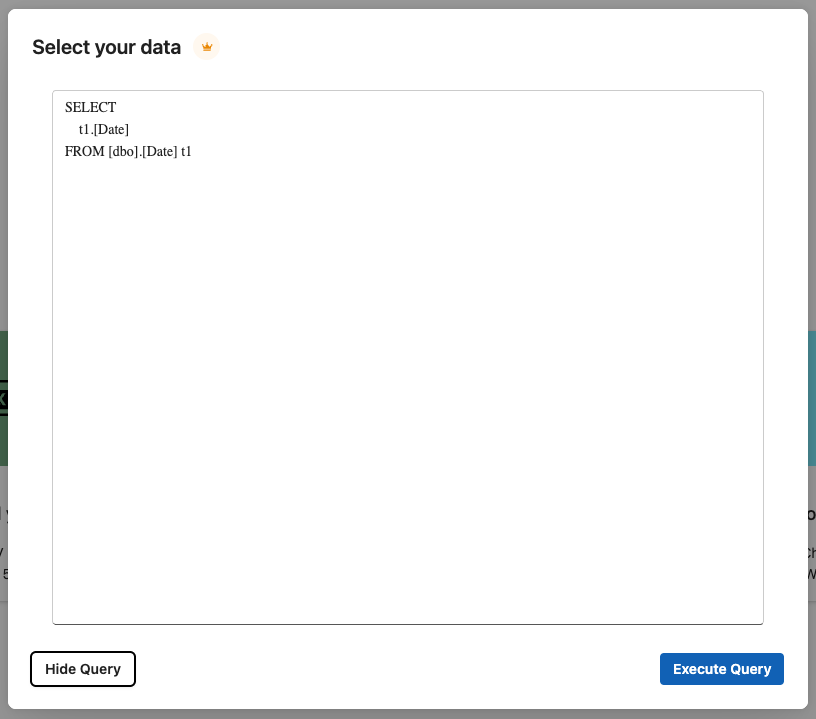
- Browse your database: databases, schemas, tables, and columns. Select columns through an interface to automatically build an SQL query in the background for data retrieval.
- Run SELECT queries only: Zebra AI blocks DDL/DML (CREATE/UPDATE/DELETE, stored procedures, etc.) to keep your data source safe.
- Large results are handled gracefully:
- Progressive retrieval with progress updates and the option to cancel long queries.
- A maximum of 10,000,000 cells (rows × columns) per query to keep the app responsive.
- If your query exceeds this ceiling, Zebra AI caps the result to the limit.
Security and privacy
- We do not store sensitive DB credentials in our database.
- For saved “SQL datasets,” Zebra AI stores only the non-sensitive connection metadata (plus your SQL query).
- Access tokens and passwords are used to establish the connection and are not persisted in our database.
- During your active session, Zebra AI may hold an encrypted, short‑lived connection token only to execute your requests; it expires with the session.
- Zebra AI disconnects and discards temporary data after the session ends.
- Any temporarily retrieved results live only for your active session and are removed automatically when the session ends or times out.
- This ensures you keep control over your source data and reduce exposure.
Using SQL data in stories
- After you connect and query, save it as a dataset to continue the same story later without reconfiguring.
- On your next visit, simply reopen the saved dataset and pick up right where you left off.
Tips for best results
- Filter and aggregate where possible to stay well under the 10M‑cell cap.
- If selecting columns through the visual interface, double check that the SQL query that gets executed is correct. Especially important on queries which join multiple tables.
- For Databricks, have your HTTP Path, Catalog, Schema, and a valid Personal Access Token ready.
- If you need to clean data deeply (e.g., standardize headers or reshape), consider exporting a file, using Zebra AI’s file cleaning assistant, then returning to your SQL workflow.
- Connectors: MSSQL, PostgreSQL, MySQL, Databricks SQL, OneLake Warehouse SQL
- Limits: 10,000,000‑cell cap; progressive fetch; cancel long queries
- Safety: SELECT-only; no writes/stored procedures
- Security: No persistent storage of sensitive credentials; short‑lived, encrypted session use only
- Retention: Temporary query results are discarded when the session ends
- Continuity: Save as a dataset to resume the same story later